Osteochondrosis is a concept used to describe a group of diseases associated with degenerative changes and dystrophy in the structure of the spine. First of all, the intervertebral disc suffers, and with the progression of the disease, the vertebrae themselves. Degeneratives are changes associated with the process of tissue wear, aging, loss of natural properties, and dystrophy - changes caused by tissue nutrition disorders. Thus, the term osteochondrosis unites most of the pathologies of the spine that are non -inflammatory in nature.
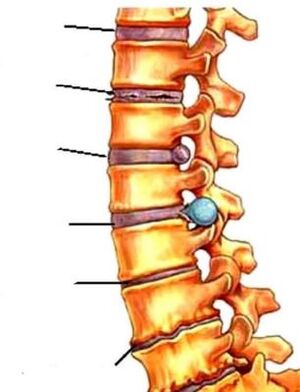
The spine forms the skeletal spine, connecting the various parts of the skeletal system. It supports the head, ribs and muscles attached to it. The spinal cord passes through the spinal space, where the brain is connected to various parts of our body. Humans are the only bipedal creatures in the world, and the spine is designed to provide bipedal movement. Thus, the spinal space has a curved shape, which is reminiscent of the letter S of the Latin alphabet and is not a rigid trunk, but a complex structure consisting of elements tied together - the vertebrae. This spinal structure allows us to perform a variety of movements, be flexible and absorb shocks and shocks. The shock -absorbing function is performed by the intervertebral disc - the cartilaginous layer made up of the nucleus pulposus and the fibrous annulus that surrounds it. The nucleus takes the load and absorbs it, and the fibrous annulus prevents the nucleus from flattening under pressure.
Decreased elasticity of the intervertebral disc can be the beginning of a variety of problems. Unable to withstand the load, the intervertebral disc begins to deform, the spine loses its proper shape. The progression of the disease leads to destruction of the intervertebral disc, ruptured fibrous rings, vertebrae in contact with each other, it becomes possible to pinch the nerves that connect the spinal cord with various parts of the body. This is how osteochondrosis develops. Intervertebral hernias occur, and inflammation often occurs. Lack of shock absorption, the spine can flatten, and together their joints form cicatricial and bone growths.
Osteochondrosis is one of the most common diseases. Only more common cardiovascular disease. According to some estimates, every inhabitant of the second planet suffers from osteochondrosis. Osteochondrosis is more common in women, but in men, the manifestations are, on average, more painful.
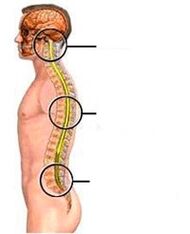
What is osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis affects various parts of the spine. Depending on which department suffers the most, there are:
- lumbar osteochondrosis - occurs most often;
- cervix - ranks second in "popularity";
- sacred;
- dada;
- widespread osteochondrosis, in which several parts of the spine are affected at once;
- cross pathology (lumbosacral or cervicothoracic).
Causes of osteochondrosis
The causes of osteochondrosis are quite diverse.
First, with age, the elasticity of the intervertebral disc gradually disappears. This means that our backs need special attention. Prolonged stay in a position that causes the spine to tilt can cause irreversible changes. You should avoid sitting in an asymmetrical position, fight the habit of lying on only one side, carrying a load (e. g. , a bag) with only one hand.
An inactive lifestyle adversely affects the health of the spine. Need to move, but physical activity should be moderate. The spine should be given a chance to recover from the load, and it is also advised to avoid injuries that also lead to the development of spinal pathology.
The second group of causes is associated with metabolic disorders and malnutrition. Foods rich in carbohydrates and fats fill the body with calories, which by us, in our inactive city life, often have no place to spend; as a result, energy is stored in the form of adipose tissue, making it overweight. Obesity is an increase in load on the spine, which leads to the development of osteochondrosis. In addition, such a diet usually contains insufficient amounts of trace elements (calcium, potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, manganese and others), which are essential for strengthening bone tissue. Being overweight is often caused by endocrine diseases. At the same time, violations of the metabolism of energy, water or minerals can also have a negative impact on the tissues involved in the structure of the spine.
Factors that contribute to the development of osteochondrosis can be:
- Flat feet;
- hormonal changes;
- contagious disease;
- local circulatory disorders,
as well as several other factors.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis
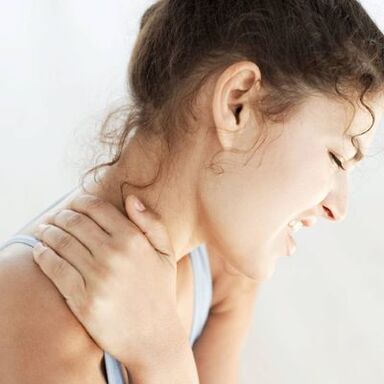
In the early stages of osteochondrosis, there are no noticeable symptoms. It is possible to assume the development of osteochondrosis if:
- dull pain in the back (in the area of the affected spinal area);
- feeling of heaviness in the back, constant tension of the spinal muscles;
- muscle numbness, the appearance of "goose bumps". In such cases, it is usually said that "his back is numb";
- cramps when turning the body and neck;
- headache, dizziness, tinnitus (usually with cervical osteochondrosis);
- pain in the chest area (usually with thoracic osteochondrosis).
At the first appearance of such symptoms, it is recommended to be examined by a neurologist.
Further progression of the disease shows uncomfortable symptoms:
Backache
There is severe pain in the back (along the spine). Pain can radiate to the limbs.
Numbness in the fingers
The typical manifestation of osteochondrosis is numbness in the fingers and toes.
Restriction of motor activity
Even with minimal physical exercise, pain increases (for example, as a result of concussions and jerks while traveling). This pain leads to significant restriction of movement and motor activity.
Methods for the diagnosis of osteochondrosis
The main role in the diagnosis of osteochondrosis belongs to instrumental studies: radiography, computed tomography, MRI.
It may be necessary to confirm that the symptoms observed are not due to another medical condition. For the purpose of differential diagnosis, general blood and biochemical tests, general urine tests, and ultrasound examination of internal organs are performed.
X-ray of the spine
X-rays are taken from problem areas of the spine. Which part needs to be examined is determined based on the patient’s complaint.
Computed tomography (CT)
Computed tomography (MSCT) makes it possible to obtain a more informative picture of the pathological process and determine its severity. In particular, MSCT makes it possible to detect intervertebral hernias.
Computed tomography was performed when X-ray data were insufficient.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
MRI is the most informative method for diagnosing osteochondrosis. In some cases (e. g. , with suspicion of thoracic spine osteochondrosis), MRI cannot be ruled out. Magnetic resonance imaging allows visualization of cartilage and soft tissues, based on which it is possible to find the source of the problem as accurately as possible and determine the cause of the disease.
Osteochondrosis treatment methods
It is best to start treatment of osteochondrosis as early as possible, as pathological changes in the spine are irreversible in most cases. Therefore, treatment is aimed primarily at relieving pain and preventing the progression of the disease.
Methods of treatment, as a rule, are complex and are prescribed individually, depending on the patient's condition. This clinic is used for the treatment of osteochondrosis:
Drug treatment
First of all, treatment aims to stop (eliminate) the pain syndrome. Anti-inflammatory and muscle relaxants (drugs that relax muscles) are used.
Also, in the treatment of osteochondrosis, drugs are used to improve blood circulation, chondoprotectors (drugs that restore cartilage tissue), vitamin D and calcium preparations.
Sort
Massage for osteochondrosis relieves muscle tone, stimulates blood flow in the spine, and improves metabolic processes. This works to strengthen the vertebral and intervertebral discs, suppress inflammation and reduce pain.
Physiotherapy
With osteochondrosis, physiotherapy methods such as electrophoresis, phonophoresis, UHF, magnetotherapy are used.
Reflexology
Reflexology for osteochondrosis is used as an adjunctive therapy method. Acupuncture helps relieve pain, reduce inflammation, normalize blood circulation, and enhance the effects of medications used.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy for osteochondrosis aims primarily to relieve pain and restore spinal mobility. A specially selected set of exercises is used.
Prevention of osteochondrosis
As a prevention of osteochondrosis, clinical doctors recommend:
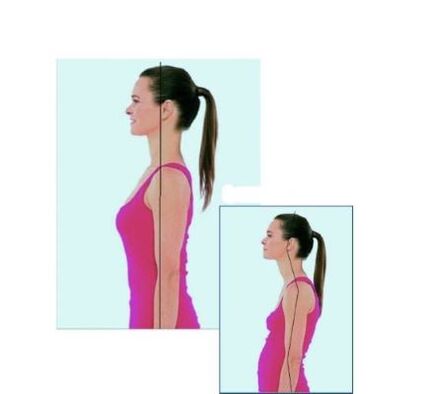
- maintain proper body posture. Posture is a normal body position while standing. Ideally, the head and back should be on the same vertical, the shoulders should be at the same level, the abdomen pulled in, and the chest lifted. Body habits are developed by exercise, therefore, body posture must be monitored - not bending or belching;
- lead an active lifestyle, do gymnastics;
- it is useful to hang on a horizontal bar - while the spinal space is stretched;
- sleep on a hard mattress. It is best to buy orthopedic mattresses and pillows;
- follow a balanced diet, eat foods that contain adequate amounts of vitamins and minerals.